SERVICE Businesses FSW (Friction Stir Welding) Division
Project overview
Here at KEIHIN RAMTECH, we introduced the FSW (friction stir welding) system earlier than most companies in Japan, and have accumulated a wealth of expertise in welding technology. We entered a licensing agreement with TWI in 2007 and have continued to achieve further technical developments. From pilot production by FSW to large-scale mass production, we can offer welding services in various materials such as copper, aluminum, magnesium, and iron. Offering a variety of technological solutions and support, we can be the perfect business partner for our customers.
We will solve the problems
you are facing!
-
Overwhelmingly better welding strength than fusion welding or other welding methods
-
Test welding and verification with sample material is possible
-
It is possible to join dissimilar materials
-
Low heat input enables welding with reduced distortion
-
We can propose existing product designs customized to FSW
Features

Welding with less strain and fewer defects than fusion welding
Good shape stability and reproducibility (no skilled worker required)
Excellent weldability by a mechanical process
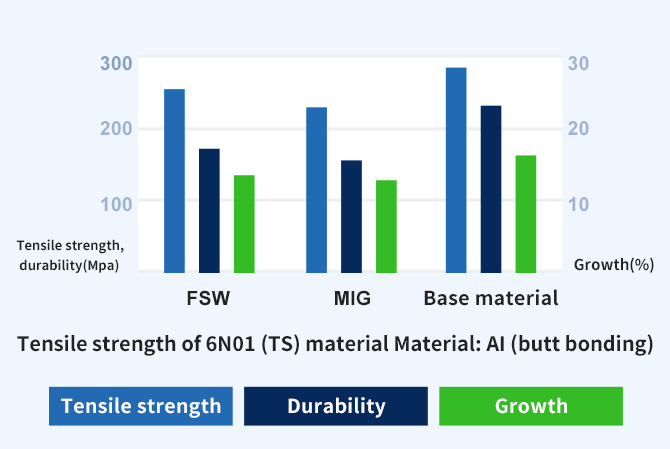
Weld strength close to that of the base material

Welding of difficult-to-weld materials
Al, Mg, Cu alloys, Fe alloys (SUS), welding between different materials
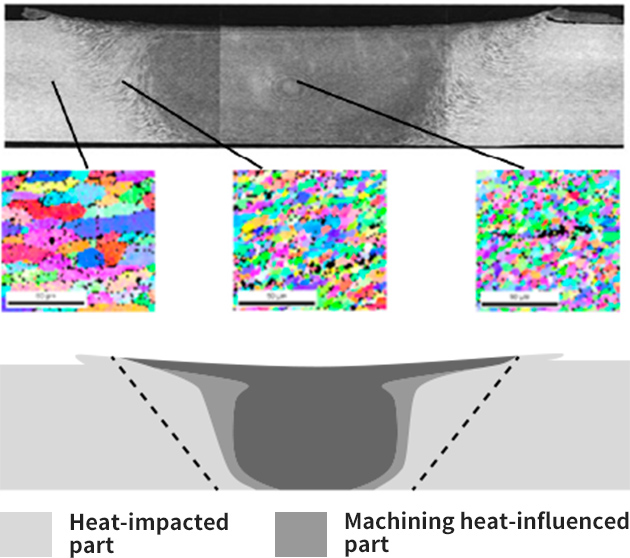
Improved environmental resistance
Unlike fusion welding, FSW is a solid phase welding process. Tig and Mig do not produce fumes or sputter. Also, power is saved because the welding is done in the atmosphere.
Features of the welded parts
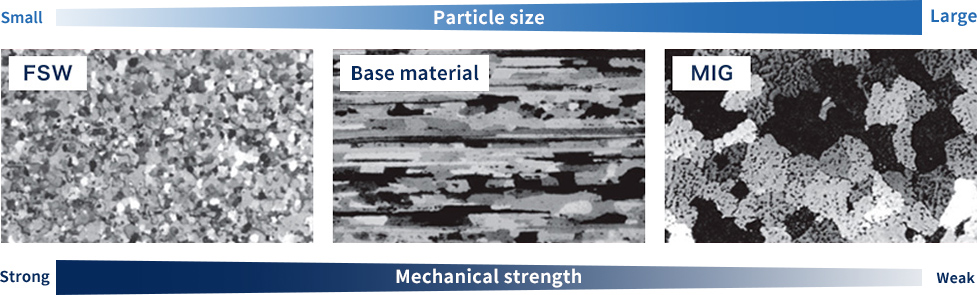
Material strength increases when the grain size is smaller, according to the Hall-Petch relationship.
For FSW
For MIG

Comparison of FSW and fusion welds
| Characteristics | FSW | Dissolution welding |
|---|---|---|
| Welding temperature (℃) |
2/3Tm | Tm or more |
| Organization | Microcrystalline tissue (without segregation) |
Molten coagulated tissue |
| Deformation | Little deformation | Large thermal deformation |
| Mechanical properties | Good | Decreased elongation |
| Energy consumed | 2/3 of fusion welding | Large |
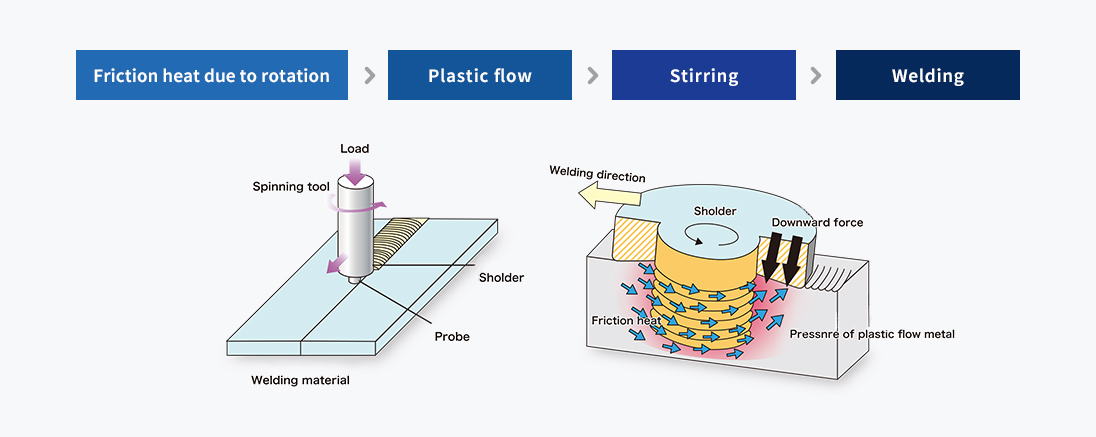
Welding principle
A rotating special tool called a probe is pressed against the material surface on the joining line. This creates a heat of friction between the probe and the material, which in turn softens the material.
Welding is performed by scanning the probe while stirring (mixing) the abutments which are in a plastic (solid) phase.
This is a [solid phase] method different from fusion welding.

Achievements and practical examples
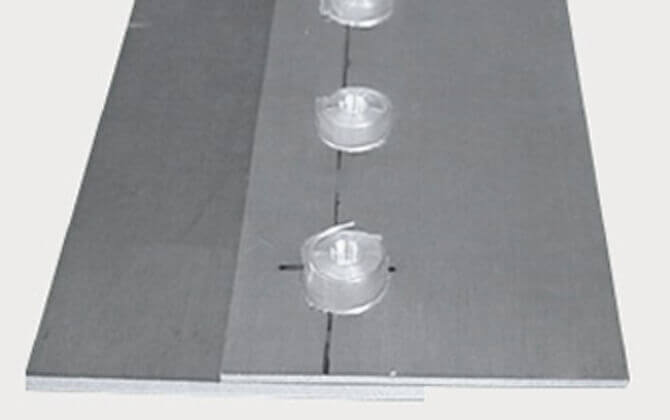
Spot welding
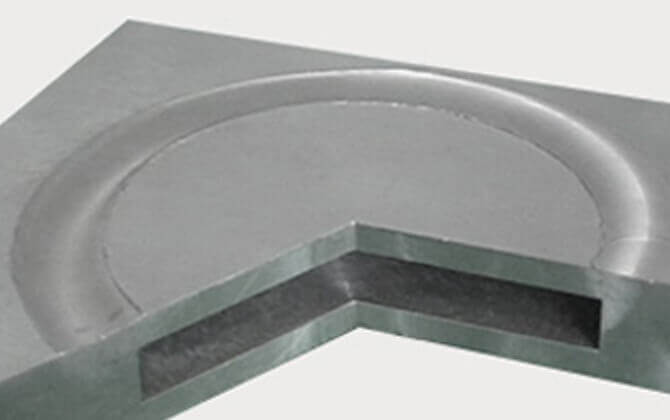
Curved butt joint

Thin-plate butt joint
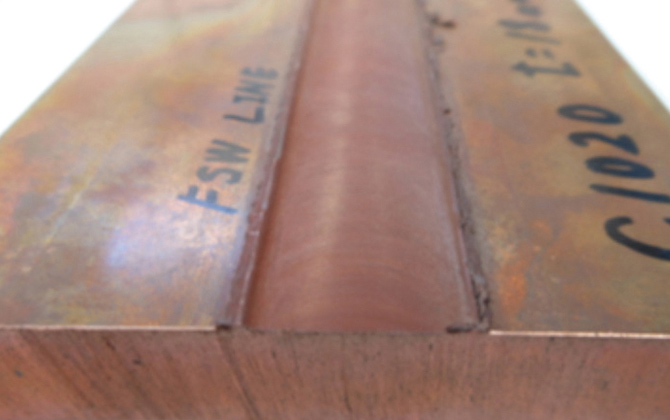

Thick-plate butt joint (Cu : 10t-40t)
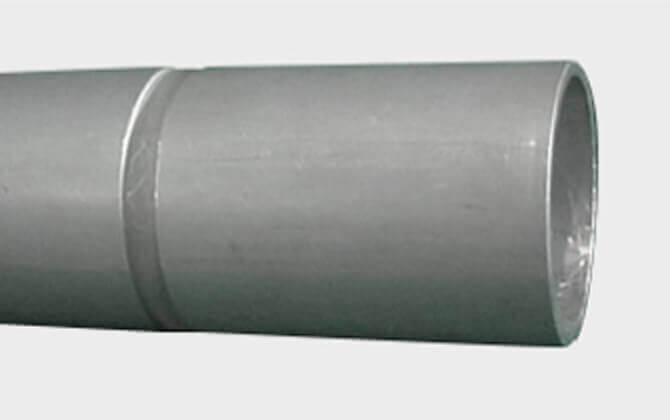

Circumference butt joint
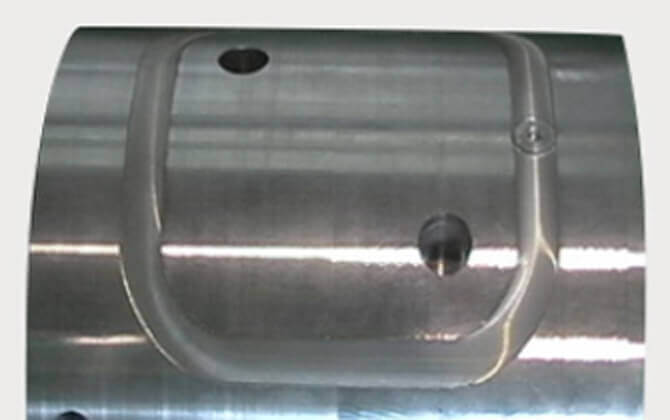

Curved butt joint
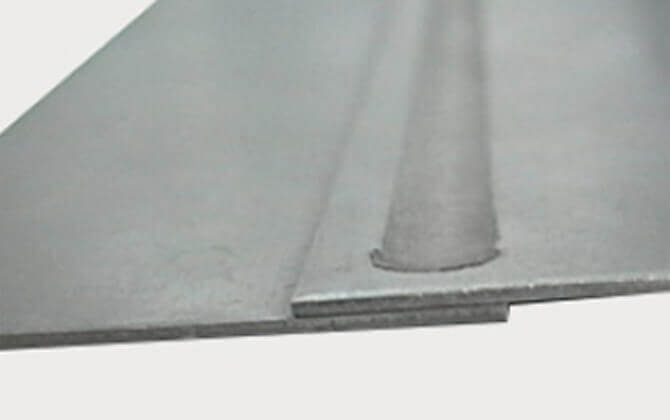
Straight lap joint
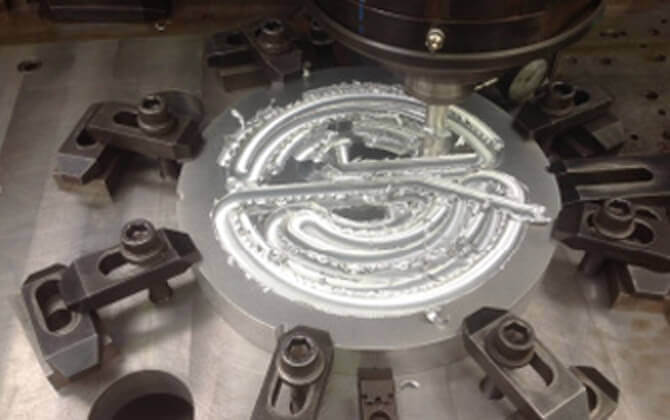

Aluminum heater joints
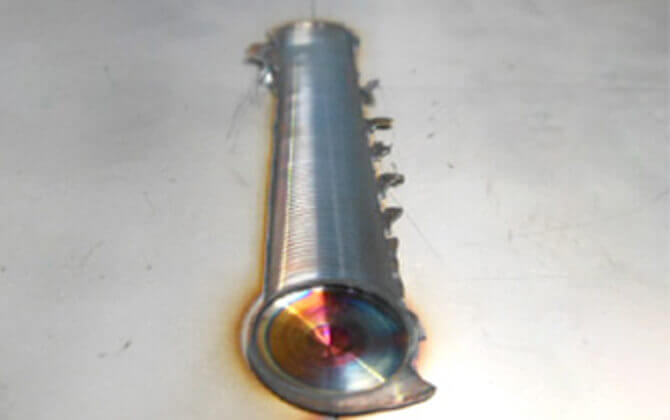

SUS304 butt joints
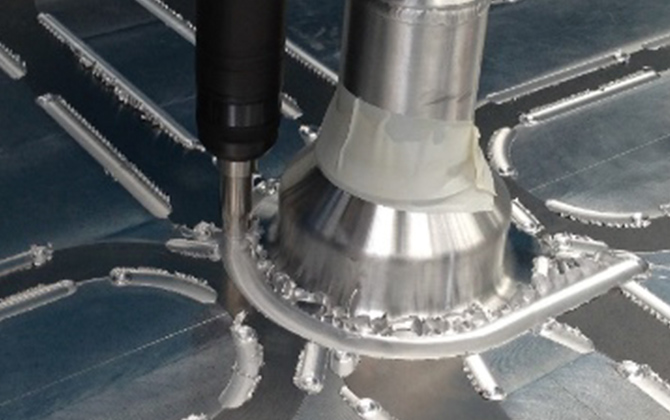

Aluminum heater joints
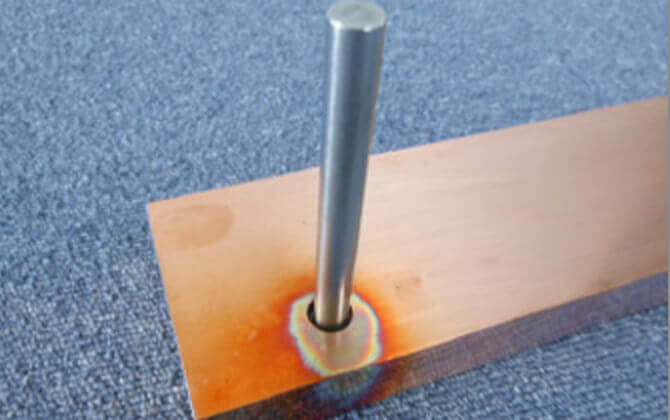

Friction welding with pressure(Cu-sus)
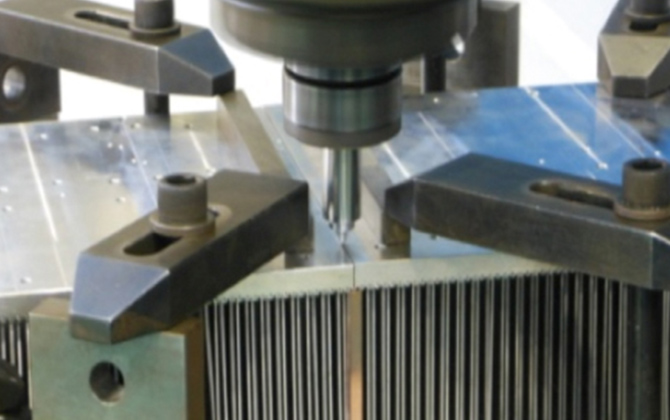

Heat sink joints
Related products

Backing plates for FPD
There is growing demand for backing plates with the expansion of the flat panel display market. Our backing plates are manufactured using unique technology and provide stable sputtering thanks to their large size, excellent flatness, and high cooling efficiency, making highly regarded by customers all over the world.
Backing plates for semiconductors
We supply a wide variety of products such as copper, Corson alloys, and chrome copper in order to support the rapid developments in integration in recent years along with the increasing speed of devices.






